Function Pointers in C++: A Practical Example
Function pointers in C++ are not just theoretical constructs; they are powerful tools that greatly enhance the flexibility and dynamism of your code. Let's delve into a real-world scenario where we utilize an array of function pointers for performing various mathematical operations!
💡 Imagine the Scenario: Dynamic Mathematical Operations
Imagine you have a task that requires performing different mathematical operations based on user input or changing requirements. Instead of relying on convoluted conditional statements, we can implement an elegant solution using an array of function pointers.
🛠️ Technical Insight: Declaration, Initialization, Invocation
Declaration
Function pointers are declared with a syntax that mirrors the signature of the functions they point to.
void (*funcPtr)(int, float);
Initialization Function pointers are initialized by assigning the address of a compatible function.
funcPtr = &someFunction;
Invocation Invoking a function through a function pointer is as straightforward as calling a regular function.
funcPtr(42, 3.14);
In this example, someFunction is a function that takes an integer and a float as arguments, and funcPtr is a function pointer that points to someFunction. When funcPtr is invoked with arguments 42 and 3.14, it calls someFunction with those arguments.
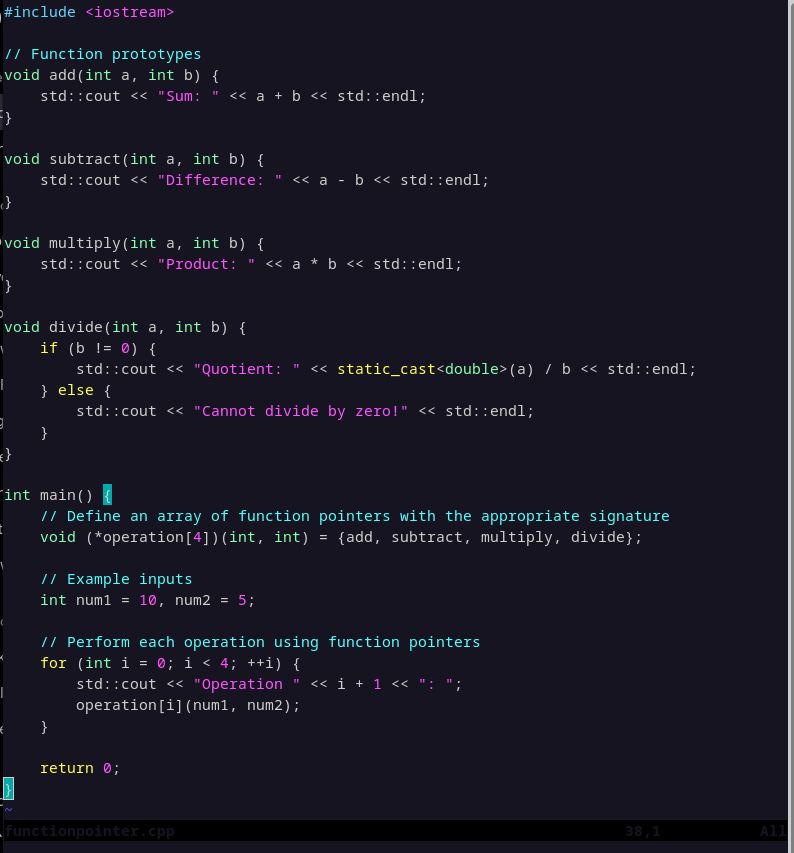
implementation
Output
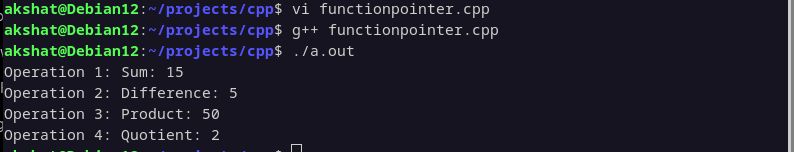
This simple yet powerful mechanism allows for dynamic and flexible behavior in your C++ code, making it easier to adapt to changing requirements and user inputs.