PSA for Developers: Hashing is NOT Encryption! Here's why it matters...
Let me share a little story with you. In my spare time, I often do JavaScript . While working on a project, I found myself struggling to differentiate between bcrypt and crypto. That got me thinking: What exactly is hashing, and how does it differ from encryption? 🤔
Hashing
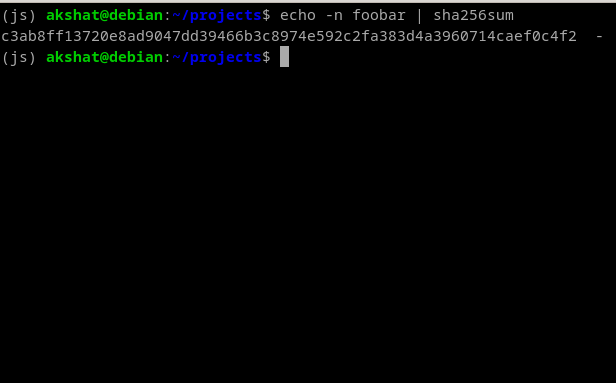
Hashing is a cryptographic technique that involves taking input data and processing it through a hash function to produce a fixed-size string of characters, known as a hash value or hash code. Common hash functions include SHA-256 and MD5.
Key Characteristics of Hashing:
One-way: Hash functions are designed to be irreversible, meaning you cannot reverse-engineer the original input data from its hash value.
Deterministic: The same input will always produce the same hash value.
Fixed-size output: Regardless of the input data size, the hash function produces a fixed-length output.
Collision-resistant: Hash functions aim to minimize the likelihood of two different inputs producing the same hash value.
Encryption and Decryption
Encryption is another cryptographic technique used to protect data confidentiality. Unlike hashing, encryption is reversible and involves transforming plaintext data into ciphertext using an encryption algorithm and an encryption key. The ciphertext can then be decrypted back to its original form using the corresponding decryption key. Examples include AES (Advanced Encryption Standard) and RSA (Rivest-Shamir-Adleman).
Why You Can't Recover Data from a SHA-256 Bit Hash:
Avalanche Effect:
Even a slight change in the input data results in a completely different hash value, making it extremely difficult to reverse-engineer the original input.
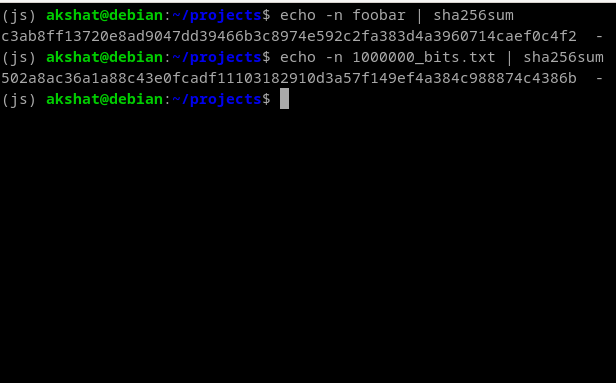
Hash functions are specifically designed for one-way encryption, meaning they transform input data into a fixed-size hash value in an irreversible manner. Unlike encryption, which is created to be reversible, storing the original data in a transformed format, hash functions compress the input data into a fixed-size output. For example, even if you input one million bits of data into SHA-256, the output will always be 256 bits. This inherent property of hash functions makes it practically impossible to reconstruct the original input data from its hash value alone. Even with knowledge of the hash value, there's no straightforward way to reverse-engineer the original data from it. While hash functions are ideal for verifying data integrity and creating digital fingerprints, they are not suitable for data recovery purposes.
Example:
SHA-256 produces a 256-bit hash regardless of the input size. Whether you're hashing a password or a massive file, the output length is the same. 1 Million bits still receive a 256-bits hash.
Conclusion
Understanding the differences between hashing and encryption is crucial for developers and anyone working with sensitive data. While both techniques play important roles in cryptography, they serve distinct purposes and offer different levels of security. If you're interested in learning more about cryptography concepts, stay tuned for our upcoming articles!